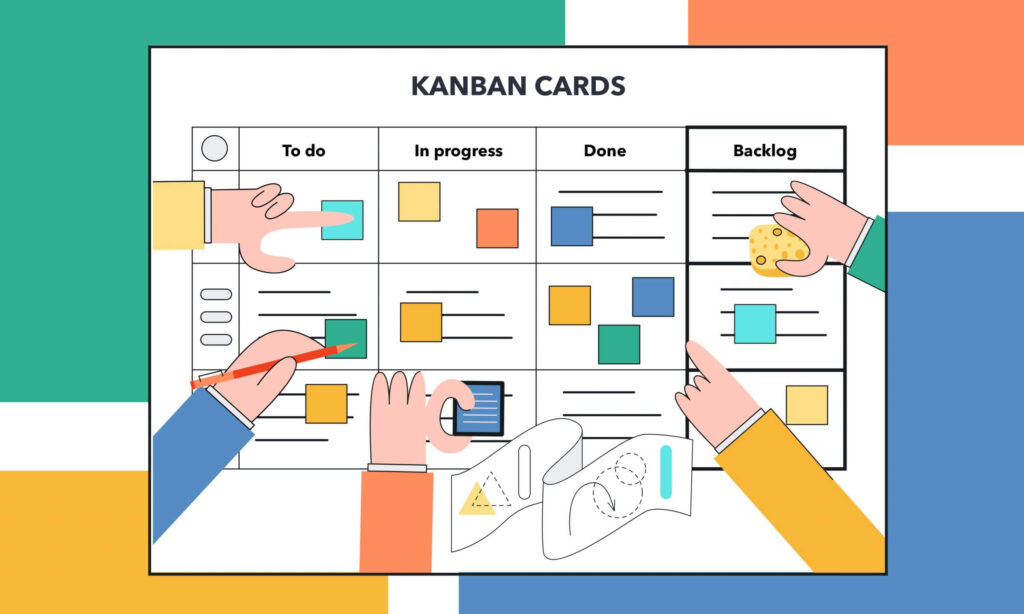
Managing projects can be difficult, especially if you’re working on multiple things at once. Juggling all of the different tasks, deadlines, and people involved can feel impossible.
Traditional project management tools like spreadsheets and whiteboards are not enough because they don’t provide an overview of all the tasks that need to be completed for a project. This can lead to important tasks being forgotten.
Fortunately, Online Kanban boards can help with project management by providing a visual overview of all the tasks that need to be completed. Tasks are represented by cards, and each card has all the information about the task, such as who is responsible for it and when it’s due.
Some leading project management software like Wrike use Kanban boards to help manage projects. Wrike’s Kanban board is fully customizable, which means you can add as many columns and swimlanes as you need to fit your project.
However, Wrike’s Kanban board is designed for large scale project management, so if you’re looking for a project manager for a small business you can check out 31 popular alternatives to wrike over here!
The origins of Kanban
Kanban is a Japanese word that means “signboard” or “billboard.” The Kanban Method is a way of managing work by visualizing the workflow and limiting the amount of work in progress. The goal is to optimize efficiency and quality by reducing waste and maximizing resources.
The origins of Kanban can be traced back to the 1940s when Taiichi Ohno, an industrial engineer at Toyota, developed a system to improve manufacturing efficiency.
The system was later adopted by other Japanese manufacturers and became known as the “Toyota Production System.”
In the 1990s, David Anderson, a software engineer, adapted the Kanban Method for use in software development. Anderson’s approach emphasized transparency, collaboration, and continuous improvement.
The Kanban Method has since been adopted by organizations in both physical kanban board and digital Kanban board forms.
What are Modern Kanban Boards?
Kanban boards are a popular tool used in agile project management. They provide a visual way to track the progress of work as it moves through each stage of the development process.
Typically, Kanban boards contain columns that represent the different stages of work, and cards that represent individual tasks. The cards can be moved between columns as the task progresses, giving team members a clear view of what needs to be done and where things are at in the development process.
Kanban boards can be used for a variety of purposes, from managing software development projects to planning marketing campaigns. In recent years, they have become increasingly popular as one of the most commonly used project management tools.
Elements of a Kanban Board
Lanes on a Kanban Board
Each Kanban board includes a number of lanes that represent the steps in your process. These lanes are typically numbered and color-coded, making it easy to see where each task is in the workflow. The number of lanes will vary depending on the complexity of your process, but most boards have between four and six lanes.
The most common lane configuration is known as the “4-step process,” which includes the following lanes: To Do, Doing, Done, and Deliverable. However, you can also add extra lanes for tasks that are “On Hold” or “Cancelled.”
By clearly identifying the steps in your process, Kanban boards make it easy to visualize your workflow and identify bottlenecks.
Kanban Cards
Kanban cards are an essential element of any Kanban board. Each card on the Kanban board represents a specific task or piece of work and provides details that make it easy for everyone on the board to understand what needs to be done.
Kanban cards can include information such as the title of the task, a description of what needs to be done, the name of the person responsible for the task, and when the task is due. In addition, Kanban cards can also be used to track the progress of a task, from start to finish.
By using Kanban cards, you can ensure that everyone on your team is always aware of what needs to be done and that tasks are completed on time.
Managing Flow with a Kanban Board
Using a Kanban board to manage your work can be an extremely effective way to stay organized and ensure that tasks are completed in a timely manner. However, for the Kanban system to be truly effective, it is important to develop some process policies that everyone on the team agrees to follow.
By doing so, you will help to keep the flow of work moving smoothly and avoid any bottlenecks or disruptions. Some examples of process policies that you might want to consider include specifying how many tasks can be in progress at any given time (WIP limits), requiring that all tasks have a completed project brief attached before moving from “To Do” to “Doing,” and setting deadlines for each stage of the project. By taking the time to establish these policies upfront, you will save yourself a lot of headaches down the road.
Types of Kanban Boards
The most popular type is the physical Kanban board, which uses sticky notes or index cards to track tasks. This can be a great way to get a visual overview of what needs to be done, but it can also be difficult to keep track of tasks if the board is not well-organized.
The other type of Kanban board is the digital Kanban board, which uses software to track tasks. This can be more convenient than a physical board, but it can also be expensive and time-consuming to implement. Ultimately, the best type of Kanban board for your team will depend on the size and needs of the business.
Kanban board examples:
1. UX Design Team Kanban Board
This type of board typically includes columns for To Do, In Progress, and Done. Each column represents a different stage of the design process.
For example, the To-Do column might contain tasks such as “research user needs” or “create wireframes.” The In Progress column might include tasks such as “conduct user testing” or “revise designs based on feedback.”
And the Done column would contain tasks such as “create final designs” or “prepare for launch.” By visually mapping out the workflow, kanban boards help team members see where they are in the process and what still needs to be done.
2. Product Board
A product board can be used to track the development of a new product, from initial brainstorming to final launch. Each stage of the product development process can be represented by a different column on the board, and cards can be used to track individual tasks.
By using a Kanban board, teams can get a clear overview of the entire product development process, and identify any potential bottlenecks. Moreover, Kanban boards can be easily adjusted as the product development process evolves, making them an essential tool for agile teams.
Kanban Boards vs. Scrum Boards
While both Scrum and Kanban boards help team members visualise task progress and identify which tasks need to be completed, there are some key differences between the two systems. First, Scrum boards are typically divided into three stages. This helps team members to see at a glance which tasks need to be started, which are currently being worked on, and which have been completed. Kanban boards, on the other hand, do not use these fixed columns. Instead, they use a flexible system of Swim lanes to show task progress.
Second, Scrum boards typically use time-based sprints to ensure that tasks are completed within a set timeframe. Kanban boards, however, do not use sprints. This allows team members to take on tasks as they are able and helps to prevent bottlenecks in the workflow.
Finally, while both types of boards can be used for individual tasks or projects, Scrum boards are typically used for larger projects that need to be completed in stages. Kanban boards, on the other hand, are often used for smaller tasks or projects that can be completed more quickly.
How to use a Kanban Board?
Kanban board is often used by project managers to track the progress of tasks. When getting started with Kanban boards the first step is to create columns, which represent the different steps in your workflow.
Then, you will have to add cards to each column. These cards can represent anything from individual tasks to larger objectives. Once you’ve added all of the cards, you’ll need to apply them to the appropriate columns.
To do this, simply drag and drop the cards into place. Finally, as you work on each task, you’ll move the corresponding card through the workflow by dragging it from one column to the next.
Benefits of a Kanban Board
Flexibility
One of the most appealing benefits of a Kanban board is the flexibility it offers. With a Kanban board, there is no need to rigidly define roles, responsibilities, and processes. Instead, each team can tailor its Kanban board to best fit its unique needs and workflows.
This flexibility allows for greater efficiency and collaboration, as team members are able to quickly adapt to changes in the Kanban board.
Reduce Downtime
Downtime is the enemy of efficiency. When workers are idle, whether due to a lack of materials or a bottleneck in the production process, it can cost businesses dearly in terms of lost productivity. Kanban boards can help to reduce downtime and keep operations running smoothly.
By visualizing the production process, a Kanban board makes it easier to identify and address bottlenecks. Moreover, the Kanban system encourages businesses to maintain a minimum level of inventory, which can help to prevent material shortages that can lead to downtime.
By reducing downtime and increasing efficiency, a Kanban board can provide a significant competitive advantage for businesses.
Increase Efficiency
By clearly displaying all of the tasks that need to be completed, as well as who is responsible for each task, a Kanban board eliminates confusion and helps keep the team focused on each individual task.
Additionally, the use of color-coded cards helps to prioritize tasks and identify Bottlenecks quickly. As a result, Kanban boards can help scrum teams to complete projects more efficiently and with less wasted effort.